- Mon - Sun 09:00 A.M - 09:00 P.M
- chettinaddentalhospital@gmail.com
Tempromandibular joint disorder (TMJ disorder) is a condition that makes your jaw painful, stiff, or unable to move fully. TMJ surgery is a process used to treat this disorder. The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a hinge-like joint where your jawbone and brain meet. It lets your jaw move up and down so you can talk, chew, and do other things with your mouth.
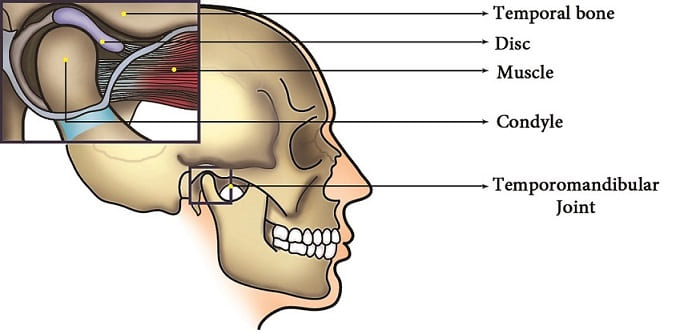
TMJ surgery is a highly specialized procedure within the field of oral and maxillofacial surgery. It requires a high level of expertise, and only the most skilled oral and maxillofacial surgeons are qualified to perform it. Mastery of this type of surgery takes years of dedicated practice. The most common surgeries involving the TMJ are those related to fractures and reconstruction of the TMJ. These surgeries are intricate and are typically performed by seasoned surgeons due to the dynamic nature of the joint, which adds an additional layer of complexity to the procedure.
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder, also known as TMD, is a group of conditions that affect the jaw joint and surrounding muscles. It can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
The exact cause of TMJ disorder is often unknown, but it may be due to a combination of factors, such as genetics, arthritis, jaw injury, or habits like teeth clenching or grinding. If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms of TMJ disorder, it’s important to see a doctor or dentist for diagnosis and treatment. There are a variety of treatments available, depending on the severity of your condition and the underlying cause.
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders are a group of conditions that affect the jaw joint and surrounding muscles. They can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain, clicking, popping, and locking.
TMJ disorders can often be managed with non-invasive treatments, such as:
Some persons, by birth, may be affected by disorders of the TMJ. In some instances, the growth of the condyle i.e. the component of the lower jaw forming a part of the TMJ may be affected.
A child’s lower jaw may sometimes be comparatively undersized than the upper jaw. This condition is termed as Micrognathia. The growth of muscles would also be simultaneously affected as the bony structure is smaller than normal. This condition could also be associated with various syndromes (Pierre-Robin’s Syndrome, Treacher Collin’s Syndrome etc). As the lower jaw is small, the tongue gets pushed backwards and tends to block the air passage. Distraction Osteogenesis is an effective treatment option to lengthen the jaw size. By this procedure the jaw can be brought to the normal size, without the necessity of bone grafting (bone harvested from hip bone to lengthen the jaw size).
In some individuals, there may be an imbalance between right and left sides of the face. This type of facial growth deformity characterized by facial asymmetry is called Hemifacial Microsomia. In this condition, the structures of one side of the face grow lesser than the other side. This results in asymmetry of the face. The affected side of the face appears disproportionately smaller than the other.
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) ankylosis is a condition in which the jaw joint fuses, restricting jaw movement and mouth opening. It is most commonly caused by trauma or injury to the joint.
Surgery is the only way to treat TMJ ankylosis.
In some cases, gap arthroplasty may be performed along with bone graft from the rib to reconstruct the TMJ joint.
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) ankylosis is a condition characterized by the immobility or fusion of the jaw joint, often resulting in a chronic, painless limitation of mandibular motion. This can make it difficult to eat, speak, and maintain oral hygiene.
TMJ ankylosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
There are three main types of TMJ ankylosis:
The main symptom of TMJ ankylosis is limited mouth opening. This can range from mild to severe. In severe cases, the mouth may be unable to open more than a few millimeters.
Other symptoms of TMJ ankylosis may include:
The treatment for TMJ ankylosis depends on the type and severity of the condition.
In some cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary.
If you are experiencing symptoms of TMJ ankylosis, it is important to see a doctor or dentist for diagnosis and treatment.
Early diagnosis and treatment of TMJ ankylosis can help to improve the outcome and reduce the risk of complications.